Table of Contents:
The basics of Reverse Osmosis
Understanding electronic reverse osmosis systems
Reveiling non-electronic reverse osmosis systems
Electronic vs. Non-Electronic RO Systems: the key differences
How to choose the right RO system for your needs
FAQs
Conclusion
As water filtration technology advances, reverse osmosis (RO) systems have emerged as one of the most efficient ways to purify water. However, regarding RO systems, there is an important distinction: electronic vs. non-electronic. Understanding the key differences between these two systems is crucial for choosing the one that best suits your needs and preferences.
This article will delve into the world of electronic and non-electronic RO systems, exploring their unique features, advantages, and disadvantages. So, let's dive in and explore the fascinating world of RO systems!
The basics of Reverse Osmosis

Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water purification technique that utilizes membrane filtration to remove contaminants from water through osmosis. In simple terms, RO works by applying pressure to push water through a semipermeable membrane, which blocks impurities like bacteria, viruses, chemicals, salts, and other water contaminants from passing through. This process results in purified water on one membrane side and concentrated pollutants on the other.
Understanding electronic reverse osmosis systems
Definition and function of electronic RO systems
Electronic reverse osmosis systems, also known as electronic RO systems, utilize advanced technology to purify water efficiently. Compared to non-electronic RO systems, electronic RO systems incorporate technological advancements that enhance their performance differences.
These systems are designed to operate with lower energy consumption while maintaining high purification levels. The efficiency comparison between electronic and non-electronic RO systems often shows that electronic systems can produce more purified water using less energy. Additionally, the maintenance requirements for electronic RO systems are usually streamlined due to automated features that monitor and adjust system functions.
Advantages of electronic RO systems
With advanced technology integration, electronic reverse osmosis systems offer significant advantages in water purification efficiency and maintenance ease. When considering electronic RO systems, you can benefit from:
- Efficiency benefits: Electronic systems often have advanced filtration processes that remove impurities.
- Cost savings: These systems are more energy-efficient, lowering electricity costs over time.
- User-friendly features: Electronic RO systems often come with intuitive interfaces and automated functions for ease of use.
These advantages showcase how electronic RO systems provide cleaner water efficiently, cost-effectively, and with user convenience in mind, reflecting the ongoing innovation trends in water purification technology.
Limitations of electronic RO systems
While electronic RO systems offer advanced water purification capabilities, they come with certain limitations that must be considered. Performance concerns may arise due to the complexity of electronic components, leading to potential issues with water production rates or quality. Reliability issues can also be a factor, as electronic systems may be more prone to malfunctions or breakdowns compared to non-electronic alternatives.
The environmental impact of electronic RO systems should be noticed, as they often consume more energy during operation. Maintenance requirements for electronic systems tend to be higher, requiring regular checks and potential component replacements. Additionally, cost considerations are essential, as electronic RO systems typically have higher upfront and maintenance costs compared to non-electronic options.
Reveiling non-electronic reverse osmosis systems
Definition and function of non-electronic RO systems
Non-electronic reverse osmosis (RO) systems operate without electronic components. They rely on water pressure to purify water through a semipermeable membrane. These systems are known for their simplicity and effectiveness in removing impurities from water.
Advantages of non-electronic RO systems
With their straightforward operation and minimal maintenance requirements, Non-Electronic RO Systems offer users a reliable and efficient way to purify water. These systems provide:
- Water Purity: Non-electronic RO Systems effectively remove impurities and contaminants, ensuring high water purity levels.
- Manual Operation: Users have more control over the purification process, allowing for adjustments based on specific needs.
- Lower Maintenance: Because these systems lack electronic components, they have fewer parts that can malfunction, resulting in reduced maintenance costs.
Non-Electronic RO Systems are also environmentally friendly and cost-effective options for those seeking a dependable water purification solution without the complexities of electronic systems.
Limitations of non-electronic RO systems
While non-electronic RO Systems offer various advantages in water purification, they also come with limitations that users should be aware of. Efficiency comparison is one significant drawback, as non-electronic systems may not be as efficient as their electronic counterparts in removing contaminants.
Water wastage is another concern, as these systems typically discard more water during filtration. Due to increased water wastage, the environmental impact of non-electronic RO systems is often higher.
Cost analysis reveals that although non-electronic systems are initially cheaper, they may incur higher operational costs over time. Maintenance requirements for non-electronic RO systems are typically more demanding, necessitating frequent filter changes and sanitation to ensure optimal performance.
Electronic vs. Non-Electronic RO Systems: the key differences
Technology and operation
The key differences between electronic and non-electronic reverse osmosis systems lie in their technology and operation. Electronic systems have seen significant technological advancements, providing advanced features for efficient water filtration. On the other hand, non-electronic systems operate using traditional methods with minimal technological integration.
Operational differences are evident as electronic systems offer automated functions, while non-electronic systems may require more manual operation. Regarding efficiency comparison, electronic systems tend to be more precise and produce higher-quality water.
Additionally, maintenance requirements vary, with electronic systems sometimes needing more frequent upkeep. Lastly, considering cost-effectiveness considerations, electronic systems may have higher upfront costs but could lead to savings in the long run.
Energy efficiency
For energy efficiency comparisons between electronic and non-electronic reverse osmosis systems, consider the power consumption differences as a key factor. When looking at energy consumption, non-electronic RO systems generally use less power than their electronic counterparts.
This can contribute to sustainability efforts and eco-friendliness. While electronic systems may offer higher performance and effectiveness, the trade-off in electricity usage should be taken into account for long-term efficiency and reliability.
Maintenance and lifespan
Considering maintenance of ro system and lifespan, electronic reverse osmosis systems typically require more frequent upkeep compared to their non-electronic counterparts. Here are some key points to consider:
- Maintenance Tips: Electronic RO systems often need specialized maintenance due to their complex components.
- Lifespan Comparison: Non-electronic RO systems tend to have a longer lifespan than electronic ones, as fewer parts can malfunction.
- Common Issues: Electronic systems may face issues with electronic components, sensors, or displays, requiring more troubleshooting.
Cost
The cost difference plays a significant role in decision-making when comparing electronic and non-electronic reverse osmosis systems. Non-electronic systems generally have lower installation costs since they're designed simpler and don't require electricity. However, electronic RO systems may offer long-term savings due to their improved energy efficiency and lower overall operational costs.
Electronic systems are more efficient in terms of energy consumption as they only use power when needed, unlike non-electronic systems that run continuously. Moreover, electronic systems often have a smaller environmental impact due to reduced water wastage. Lastly, electronic RO systems tend to have higher performance efficiency, consistently providing better-quality purified water.
How to choose the right RO system for your needs
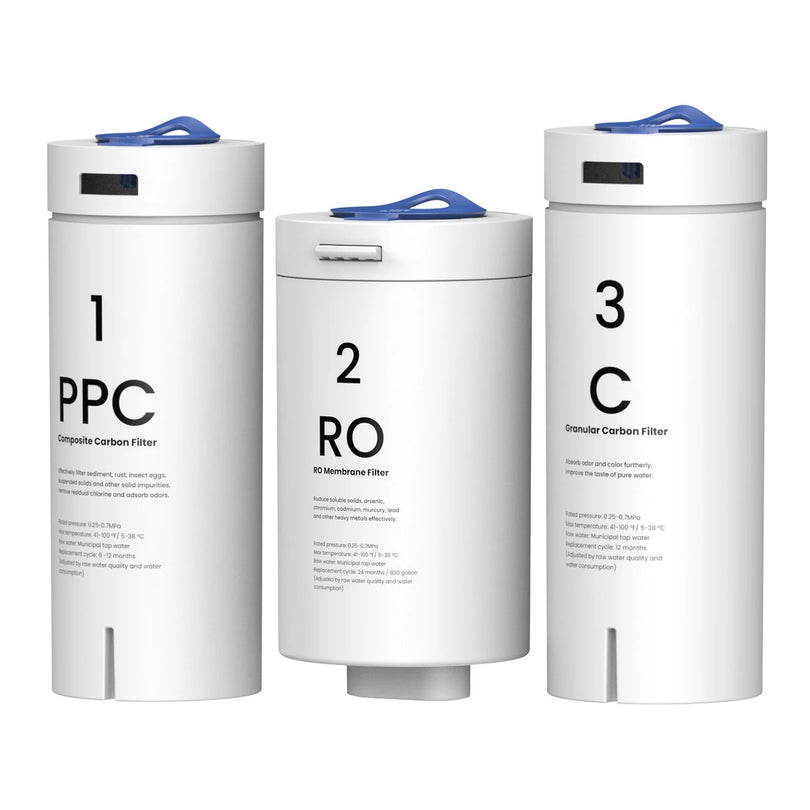
Selecting the appropriate RO system like Undersink RO Water Filter System for your specific requirements can greatly enhance the quality of your water. When choosing the right RO system, consider the following factors:
- Filter selection: Ensure the system has suitable filters to address contaminants in your water source.
- Water quality: Assess your water's quality to determine the filtration level needed for optimal results.
- Installation process: Consider the ease of installation and whether professional help is required.
- Budget considerations: Evaluate the initial cost, maintenance expenses, and any additional costs associated with the system.
- Long-term durability: Look for systems with good reviews regarding their longevity and durability to ensure a lasting investment.
FAQs
Is electronic RO better than non-electronic RO?
Performance comparison shows that electronic RO systems often offer faster filtration rates and higher water production than non-electronic ones. However, electronic RO systems generally come with a higher initial cost, which should be factored into a cost analysis when deciding between the two.
Do non-electronic RO systems require more frequent filter replacements than electronic systems?
Due to their design and operational differences, non-electronic RO systems may necessitate more frequent filter replacements than electronic systems. Electronic systems offer more automated monitoring and adjustment capabilities, potentially extending the lifespan of filters.
Conclusion
So, when it comes to choosing between electronic and non-electronic RO systems, it ultimately boils down to your specific needs and preferences. Electronic systems offer convenience and automation, while non-electronic systems are simpler and more cost-effective.
Consider factors like water usage, budget, and maintenance requirements before deciding. Whichever option you choose, both types of RO systems can effectively purify your water and provide clean, safe drinking water for your home. Follow Glacier Fresh to find more water filtration solutions.